It's no secret - data-driven marketing has become more accessible and, thus, critical to keeping pace within your industry.
Data-driven marketing is all about gathering the right kind of data, processing it, and uncovering insights to make informed decisions about your marketing strategy, preferably before your competitor gets to it first.
Table of Contents
A well-marketed business will inevitably curate many touchpoints customers can interact with that a vast and virtually inexhaustible amount of data signals are simultaneously generated by the second. Understanding how to track and measure every aspect of your marketing efforts and visualize your performance in real time has become essential! There is a quote from John Wanamaker in the late 1800s – does it resonate with where your business is at the moment?
Half the money I spend on advertising is wasted; the trouble is I don't know which half.
What is Data Attribution?
Data attribution is the process of assigning credit to a particular marketing channel or touchpoint for a conversion or sale. Understanding data attribution is essential as it allows you to understand which channels drive the most value and allocate your campaign budgets accordingly.
To further illustrate this, consider the customer journey examples and how data attribution plays a role in determining future campaign goals:
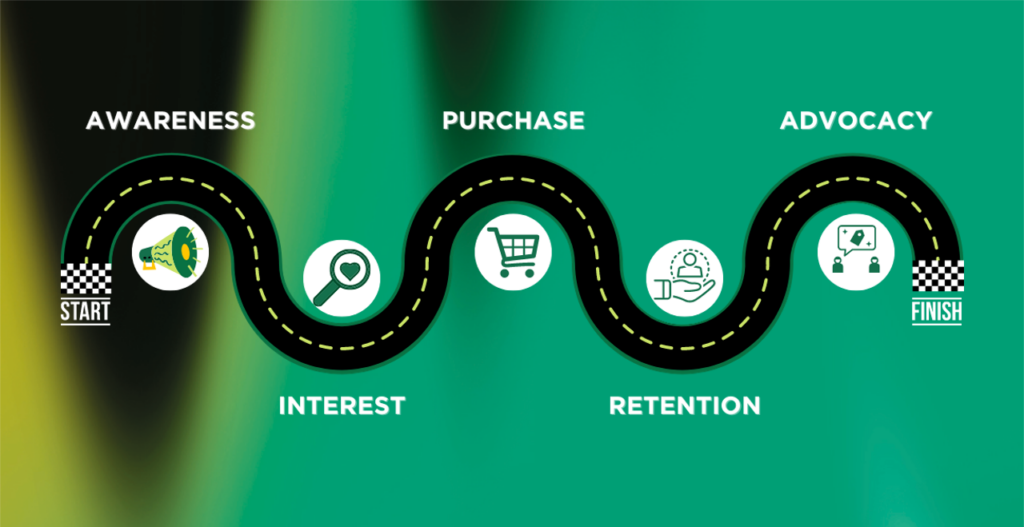
Funnel of an E-commerce Store
To illustrate the importance of data attribution, let’s look at the funnel of an online e-commerce store. At the top of the funnel, you might have a Facebook awareness or branding ad that drives a new audience to your website or generates brand awareness. From there, the potential customer might start looking for Youtube product reviews, recalls your branding campaigns, and clicks on a Google display or search ad they saw as they explore all options in the market. The user might sign up for your newsletter to keep updated on future offers you might run and finally convert through an email campaign.
By retroactively assigning credit to each touchpoint, you can better understand which channels drive the most value and adjust your marketing efforts accordingly. This might involve shifting your budget to focus more on Facebook ads to boost awareness, increasing your Google search campaigns to increase your position during the purchase intent stage, or optimizing your email campaigns to increase your conversions. This could also help you optimize your landing pages to increase sales or test different ad creatives to improve click-through rates.
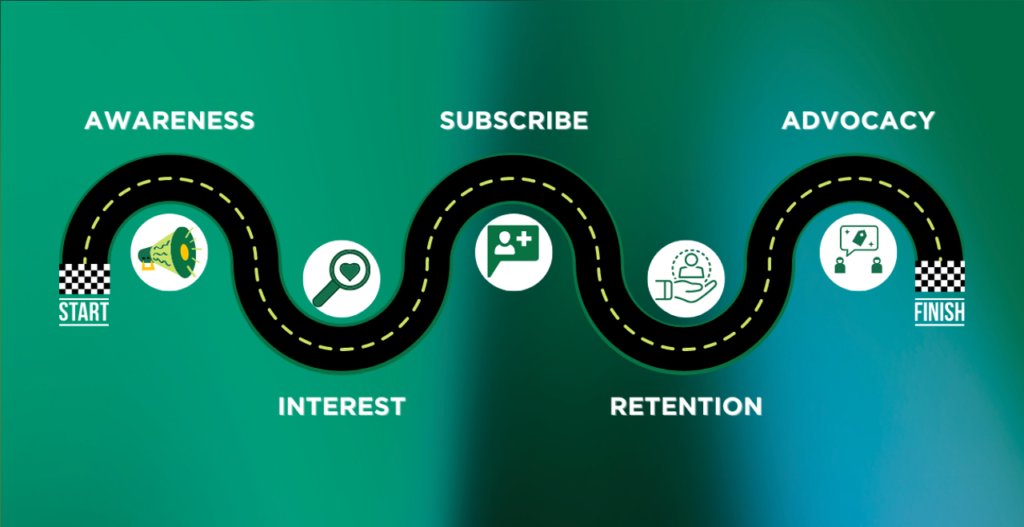
Funnel of a SAAS Company Using a Subscription Model
On the flip side, the funnel of a SAAS (Software as a Service) product using a subscription model is a bit different. At the top of the funnel, you still have brand awareness ads on Social Media and Programmatic channels that drive traffic to your website. Google search ads also are crucial during the offer evaluation stages. From there, the customer might sign up for a free trial, become a paying customer, and eventually churn.
Churn is an essential consideration for SAAS companies using a subscription model. By tracking the customer journey and assigning credit to each touchpoint along the way, you can gain insights into why customers are churning and take steps to reduce churn and improve customer retention. This might involve optimizing your onboarding process or creating targeted campaigns to re-engage customers at risk of canceling their subscriptions.
The 3 Foundations of Attribution
Now that we know what we want to achieve by introducing data attribution within your marketing funnels let’s run through the critical foundations to achieve this.
Any Data Consolidation and Governance projects can feel like a large endeavour for any team size. Championing this goal might also feel daunting to achieve without research and guidance.
We’ve distilled years of experience into three foundations you need. In the following section, we will guide you through the blueprint that enables you to capture all the necessary data signals to inform you of your next strategies.
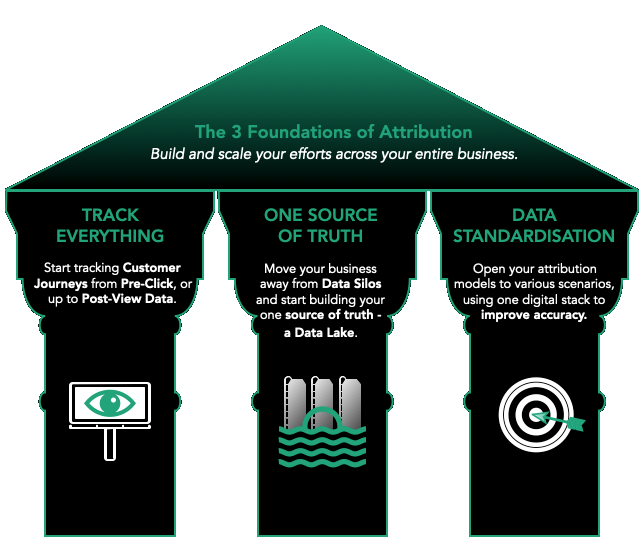
Track Everything : Including Post View Tracking

Post-View Tracking
Many businesses of various sizes often overlook post view tracking. Post View tracking involves accumulating data on the customer’s behavior as they see your advertisment.
This might include data on the sites the users saw your ad, including data signals from their browsing behavior, and understanding which ad and placement setup increased your visibility. By collecting this data, you can gain a far more profound understanding of the customer’s intent, where your most valuable customers usually hang out on the web and explore the user’s sentiment toward the brand as they view your ad and offers.
Post-view tracking benefits brand exposure campaigns, aiming to increase brand awareness and reach a broader audience. By understanding how customers interact with your brand at the ad impression level, you can create more effective campaigns tailored to their needs and interests, enhancing engagement, recall, and better traffic to your landing pages.

Post-click Tracking
Post-click tracking involves tracking every touchpoint in the customer journey after the customer clicks on an ad and visits your site.
This might include tracking website visits, clicks, conversions, and more. Collecting data on each interaction allows you to assign credit to each touchpoint based on its perceived impact on the conversion. This will enable you to understand better which channels are driving the most value by analyzing the source of the traffic. An easy setup for this is by using UTMs in your links.
Post-click tracking is often done using tools like Google Analytics, Matomo, and Adobe Analytics. By using these tools, you can collect data on website visits, clicks, conversions, and more. You can more closely analyze user behavior by implementing heatmaps and screen recordings on your site. Tools like Matomo and HotJar can be great platforms to leverage here.
One Source of Truth: Seek to build Data Lakes, not Data Silos
The biggest hurdle for any business tackling proper value attribution across all its touchpoints is when it operates on data silos.
When different departments or teams use various tools or platforms to track their marketing efforts, getting a clear picture of what’s working and what’s not can be challenging.
Think about this dilemma. Assuming you have a successful affiliate team, an internal SEO team, and you’ve signed an advertising agency to help you in your outreach. Attributing the proper weighting to each touchpoint will allow you to audit each Marketing activity your business is engaging in while avoiding issues such as:
- Overpaying commissions to your affiliate partners. Affiliates are great at driving the right customer to you as effectively as possible. Usually, affiliate review and comparison sites are the last touchpoints before a visitor commits to a sale. Does this warrant excluding all other efforts from the mix?
- Ascribe a proper value to your Top-funnel efforts, such as branding, and assess its trickle-down effect on Affiliates and SEO projects. Is there an uplift seen across all touchpoints? Can you renegotiate terms with your affiliates to lower costs but maintain performance?
- Uncover customer trends you might have missed if data remained under Silos. As all touchpoints become accountable, when unified, you will be able to observe both the bigger picture and the little underlying intricacies that build it up. Could audience niches discovered in the branding and awareness stages inform your Search Engine Marketing strategies? Or vice versa?
The answer you seek here is to move away from data silos and start building your data lake.
A data lake is a centralized repository of data that allows you to store and manage your business data in one place, formed through multiple data sources, including Marketing data. Building and using a data lake, allows you to quickly analyze data from different sources and gain insights into your marketing efforts across channels and touchpoints. This allows you to make data-driven decisions and optimize your marketing strategy for maximum impact.
Data lakes are especially useful when working with multiple marketing channels, such as social media, email marketing, and paid advertising. By consolidating your data into a single location, you can view your marketing efforts holistically and better understand how each channel contributes to your overall success.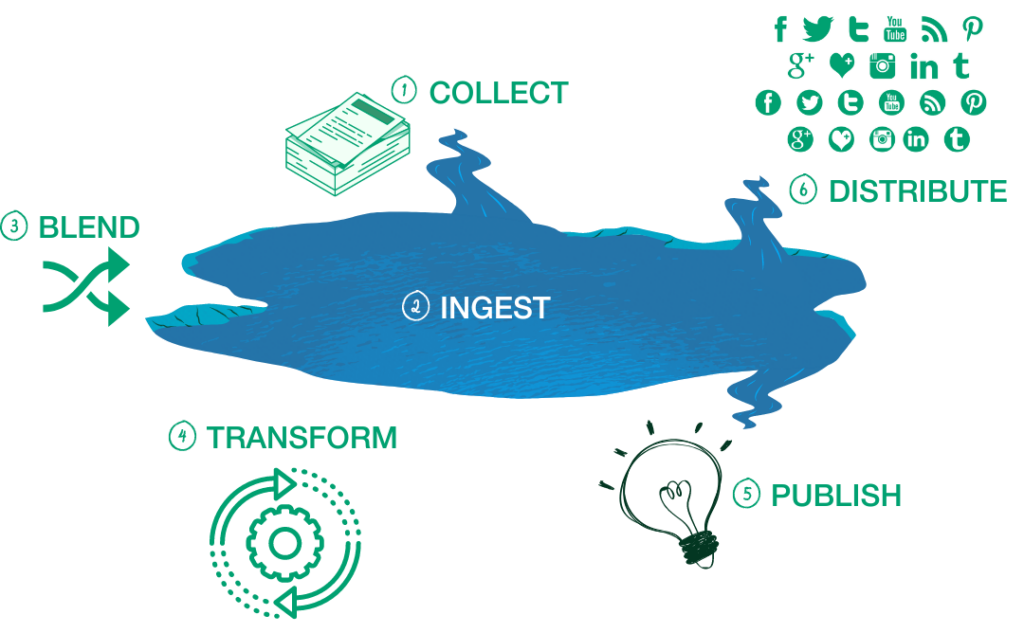
Steps to build your Data Lake
How to build a Data Lake?To build a data lake, you’ll need to follow a number of steps, including collecting data, ingesting it into the data lake, blending it with other data sources, transforming it into a usable format, and publishing and distributing it to your team.

Collect Data
The first step in building a data lake is to collect data from all of your marketing channels and touchpoints. This might include data from social media, email marketing, paid advertising, and more. It’s important to collect as much data as possible to get a complete picture of your marketing efforts.
Ingest Data
Once you’ve collected your data, you’ll need to ingest it into your data lake. This involves loading the data into a storage system, such as Google Big Query, Hadoop or Amazon S3. It’s important to choose a storage system that can handle the volume and variety of data that you’re working with.

Blend Data
After ingesting your data, you’ll need to blend it with other data sources to gain a more complete picture of your marketing efforts. This might involve blending data from different marketing channels, as well as data from other sources, such as customer relationship management (CRM) systems. Check out our Data Standarization section for deeper insights.

Transform Data
Once you’ve blended your data, you must transform it into a usable format. This might involve cleaning the data, formatting it, and structuring it to make it easy to analyze. You may also need to enrich your data with additional information, such as customer demographics or geographic data.

Publish and Distribute Data
Finally, you’ll need to publish and distribute your data to your team. This might involve creating dashboards or reports that make it easy to visualize and analyze your data. You may also need to provide access to your data lake to other teams or departments within your organization.
By following these steps, you can build a data lake that provides a comprehensive view of your marketing efforts, allowing you to gain valuable insights into which touchpoints are driving the most value and optimize your marketing strategy accordingly.
A Data Lake is a large project that requires a serious investment of time, money, and talent. Commitment across the entire organization is essential, and starting with communicating the mindset and championing the cause is a good start. Another more tangible goal you can facilitate to kickstart the process is Data Standardization.
Data Standardization
The key to a healthy organization-wide Data Lake is ensuring your data follows a standardized protocol that unifies and tracks your channels under granular variables (clicks, impressions, views, and email opens) and matches them to the business’s goals (signups, registrations, sales, deposits). Essentially creating a seamless customer path with each touchpoint present and accountable towards the overarching business goals. As we saw in the previous section, when different departments or teams use various tools to track their marketing efforts, ensuring that your data is consistent and accurate can be challenging.
Some examples of how to establish clear data standards and protocols might involve:
By standardizing your data, you can ensure that it’s consistent and accurate across all of your efforts, enabling your data to be streamed into your Data Lake seamlessly and then queried uniformly to extract fully detailed customer paths. Once you build the foundational infrastructure to track the bare necessities, you can explore other facets of data, such as more complex audience data, which you can include to enrich your understanding of your ideal customer.
So as Performance Marketers ourselves, focused on Search Engine Marketing and Programmatic/Display buying partners, what tools do we rely on? Our platform-of-choice is Google’s Marketing Platform which in it’s offering contains:
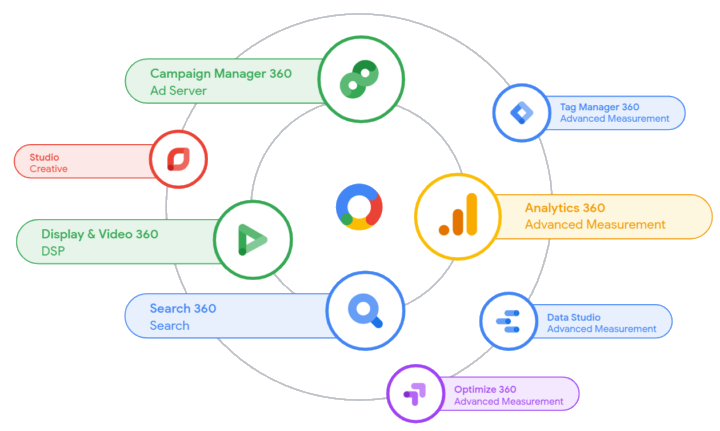
The Google Marketing Platform creates one universal language for all your marketing efforts, allowing you to consolidate all our advertising channels into one standardized funnel. Using Google Campaign Manager’s Floodlight Tag technology to collect conversion data centrally, you can attribute conversions to all trafficked channels. The Marketing team can then rely on one data API export for all your marketing data to deliver one unified data stream into the organizational Data Lake. Essentially with this solution, you would have tackled data standardization on all your media channels.
Selecting Your Attribution Model
Now to the final stage, the analysis stage. Once your setup is complete, it is time to select the model to use in order to assign value. There are two types of attribution models, based on the number of touchpoints you wish to attribute. Let’s explore in the coming section:

Single-Touch Models
Single touchpoint attribution assigns all the credit to one touchpoint in the customer journey. While single touchpoint attribution is simple and easy to understand, it can be misleading as it oversimplifies the customer journey and fails to capture the impact of other touchpoints. Models under this category include:
First-Touch Attribution
First-touch attribution is one of the most straightforward approaches to data attribution. This approach assigns 100% of the credit for a conversion to the first touchpoint in the customer journey. First-touch attribution is helpful when you’re auditing your Branding and CPV campaigns. For example, if a customer first interacts with your brand through a Branding ad and later goes on to make a purchase, first-touch attribution would assign all of the credit for that sale to the Programmatical Branding ad.
While first-touch attribution is simple, it can be misleading. It doesn’t take into account the other touchpoints in the customer journey that may have contributed to the sale.
Last-Touch Attribution
Last-touch attribution is the opposite of first-touch attribution. This approach assigns 100% of the credit for a conversion to the last touchpoint in the customer journey. This model is used in assessing which channel is instrumental to convert users in your funnel. For example, if a customer first interacts with your brand through a Facebook ad and later goes on to make a purchase after clicking on a Google search ad, last-touch attribution would assign all of the credit for that sale to the Google search ad.
Like first-touch attribution, last-touch attribution can be misleading. It doesn’t take into account the other touchpoints in the customer journey that may have contributed to the sale.
Last-non-direct-click attribution
Last-non-direct-click attribution assigns credit to the last touchpoint that the customer interacted with before converting, except for direct traffic. This attribution model can to leveraged to analyse bottom-funnel data to inform your top-funnel strategy. For example, if a customer first interacts with your brand through a Facebook ad, clicks on a Google search ad, and finally converts after visiting your website directly, last-non-direct-click attribution would assign all of the credit for that sale to the Google search ad.
This approach is useful because it gives credit to the touchpoint that is most likely to have contributed to the conversion, while also excluding direct traffic, which may not be a reliable indicator of the customer’s intent. However, it may not always provide a complete picture of the customer journey and may overlook touchpoints that contributed to the conversion indirectly.
Multi-Touch Models
In contrast to a Single-touch attribution model, multi-touch attribution distributes credit to multiple touchpoints based on their perceived impact on the conversion. Multi-touch attribution provides a more nuanced view of the customer journey, allowing marketers to understand which touchpoints are driving the most value and to optimize their marketing efforts accordingly. This approach also helps to identify customer pain points and areas of improvement in the customer journey, providing valuable insights for businesses seeking to improve their overall customer experience. Models under this category include:
Linear Attribution
Linear attribution is a data attribution model that assigns equal credit to each touchpoint in the customer journey. For example, if a customer first interacts with your brand through a Facebook ad, then clicks on a Google search ad, visits your website, and finally converts through an email campaign, you might assign 25% of the credit to the Facebook ad, 25% to the Google search ad, 25% to the website visit, and 25% to the email campaign.
The idea behind linear attribution is that each touchpoint in the customer journey is equally valuable and contributes to the overall success of the marketing campaign. This approach is useful for businesses that want to take a more balanced approach to data attribution and avoid overemphasizing any particular touchpoint.
However, it’s important to note that linear attribution may not always be the best approach for every business. Depending on your marketing goals, target audience, and marketing channels, you may need to adjust your approach to data attribution accordingly.
Time Decay Attribution
Time decay attribution is a more nuanced approach to data attribution. This approach assigns credit to each touchpoint in the customer journey, with more credit given to touchpoints that are closer to the conversion. For example, if a customer first interacts with your brand through a Facebook ad, then clicks on a Google search ad, and finally converts through an email campaign, you might assign 20% of the credit to the Facebook ad, 30% to the Google search ad, and 50% to the email campaign.
The idea behind time decay attribution is that touchpoints closer to the conversion are more valuable than those further away. This approach considers the entire customer journey and provides a more accurate picture of which touchpoints drive the most value.
U-Shaped Attribution
U-shaped attribution is another data attribution approach that considers the entire customer journey. This approach assigns 40% of the credit to the first touchpoint, 40% to the last, and 20% to the touchpoints in between. The idea behind U-shaped attribution is that the first and last touchpoints are the most valuable, while the touchpoints in between are less valuable but still contribute to the conversion.
For example, suppose a customer first interacts with your brand through a Facebook ad, clicks on a Google search ad, and finally converts through an email campaign. In that case, you might assign 40% of the credit to the Facebook ad, 20% to the Google search ad, and 40% to the email campaign.
Data Driven Attribution
Data-driven Model uses machine learning to assign a percentage of credit to each touchpoint in the customer journey based on its perceived impact on the conversion. For example, if a customer first interacts with your brand through a Facebook ad, then clicks on a Google search ad, and finally converts through an email campaign, you might assign 40% of the credit to the Facebook ad, 30% to the Google search ad, and 30% to the email campaign.
Data-driven modelling is a more flexible and highly effective approach, customised to your business’s specific needs. It’s important to note that this approach is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and you may need to adjust your weighting based on your business goals, target audience, and marketing channels. The success of this model is based on the data that is used to train it. Here the old adage applies: “Garbage-In, Garbage-Out”.
Read more on how to use Data Driven Attribution and AI in your business.
Which Attribution Model should you use?
While every case might require a varied approach, an informed answer to the question is not which attribution model to use exclusively but how to assess your marketing efforts with each available model. While individually, each attribution model has its share of pros and cons, leveraging the different viewpoints each model gives you can be crucial to finding different tactics to outperform your market rivals.
Remember: By using the right tools, you can ask more profound questions to get more insightful answers.
Enabling AI in your Marketing
Data attribution is just one part of a larger ecosystem of data-driven marketing. One of the most exciting developments in this ecosystem is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize marketing efforts. By combining data attribution with AI, your business can create a more personalized and effective marketing strategy that drives more paying users over to you.
As we’ve discussed in other sections, the key to enabling AI in your marketing efforts is to collect data on every touchpoint in the customer journey. Once this data has been collected, it can be used to train machine learning models that can help optimize marketing campaigns in real-time.
Here’s some examples you can aspire for:
- You can use machine learning to predict which marketing channels are most likely to convert a customer based on their behavior and past interactions with the brand. Following a training period, the AI built on your marketing channels will start optimising your performance automatically, managing budgets more efficiently and day-in, day-out bid on an audience profile it identified as more relevant to your campaign goals.
- Another way you can use AI in your marketing efforts is to personalize content and messaging based on the user’s interests and behavior. By analyzing data on customer behavior, you can create highly personalized content and messaging that resonates with the customer and drives engagement. The pitfall here is when message personalisation creeps into the private lives of individuals. You want to aim for convenience and relatability rather than making them feel spied on for a quick sale.
- Businesses might use machine learning to analyze customer data and create targeted email campaigns that are tailored to the customer’s interests and preferences. Think being able to reach the right person, at the right time with a crafted message just for them. Now scale it up into an automated process with minimal intervention and you’ve hit jackpot!
- Alternatively, you might use machine learning to personalize website content based on the customer’s behavior, such as showing product recommendations based on past purchases, which game they liked playing the most or which genre of movie they indulge most in – looking at you Netflix.
By combining data attribution with AI, businesses can create a more comprehensive and effective marketing strategy that drives results. Machine learning models can help businesses optimize their marketing efforts in real-time, allowing them to focus on creating high-quality content and engaging with their customers.
Conclusion
Data attribution is a critical component of any data-driven marketing strategy. By understanding the various approaches to data attribution, implementing data-driven tracking, and using tools like data lakes and pre-impression tracking, you can gain valuable insights into your marketing efforts and make more informed decisions about where to allocate your budget.
Remember, accurate data attribution requires a comprehensive approach that considers all of the touchpoints in the customer journey. By doing so, you can improve the effectiveness of your marketing efforts and drive more value for your business.
Do you have any questions on how to start your data attribution projects? At VANE IVY, we use our extensive background in data and marketing to help you and your team to expedite your process. Give us a shout!


